A Market Under Pressure
Chinese aftermarket auto parts are flooding the U.S., cutting prices so aggressively that domestic manufacturers are being squeezed out. Once dominated by U.S. and European suppliers, the industry is now seeing a rapid rise in Chinese imports, with products often priced 30–60% lower than their American counterparts.
This shift is driven by China’s cost advantages, aggressive expansion strategies, and gaps in U.S. regulatory enforcement. Chinese manufacturers leverage:
- Ultra-low-cost production and automation to produce parts at half the cost of U.S. firms.
- E-commerce loopholes that allow parts to enter the country without quality inspections, exposing consumers to safety risks.
- Transshipment tactics to circumvent U.S. tariffs, masking true product origins.
For U.S. auto parts manufacturers, these dynamics have created severe pricing pressure, supply chain disruptions, and regulatory headaches. The impact is being felt across multiple aftermarket categories, from brake systems to suspension components—but one of the hardest-hit segments is aftermarket exhaust systems and we’ll explore that as a case study in this article.
Market Growth & Competitive Strategies
Chinese auto parts manufacturers have rapidly expanded their footprint in the U.S., growing from 2% market share in 1995 to over 40% today across various aftermarket segments. Their dominance has been achieved through:
- Low-cost production: Chinese firms benefit from sheer volume, vertical integration, higher automation (12:1 robot-to-worker ratios), and raw material access at a fraction of U.S. prices, not to mention lower labor costs. Leading exporters like Shanghai Jiawen Performance Industries and Guangzhou Dekadi Auto Accessories produce exhaust systems at 50% lower costs than U.S. competitors.
- E-commerce proliferation: Platforms like AliExpress, Temu, and Amazon have enabled direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales, bypassing traditional retail channels and regulatory oversight. Over 58% of Chinese aftermarket parts now enter the U.S. through e-commerce, with 98.7% of shipments evading CPSC inspections due to the $800 de minimis rule.
- Tariff evasion tactics: Chinese firms transship goods through intermediary countries such as Thailand and Mexico, falsely labeling origins to circumvent 27.5% U.S. tariffs.
Regulatory Blind Spots & Enforcement Challenges
The influx of Chinese auto parts has created regulatory and safety concerns. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), failure rates for Chinese aftermarket parts, including critical components like brakes and steering systems, are 3.2 times higher than OEM equivalents. Despite this, enforcement mechanisms remain weak due to:
- HTS Code Misclassification: A 2024 bipartisan investigation found that 72% of Chinese aftermarket shipments had incorrect tariff codes, leading to over $1.2 billion in lost U.S. manufacturer revenue annually.
- Recall Limitations: Many Chinese sellers dissolve their U.S.-based LLCs after selling defective products, preventing the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) from enforcing recalls.
- Connected Vehicle Risks: Chinese vehicle connectivity systems (VCS) have raised national security concerns, with investigations revealing the capability to disable vehicles remotely via over-the-air updates.
While connected vehicle security risks are a growing concern, the more immediate regulatory gap is the lack of enforcement on safety compliance for aftermarket parts.
Case Study: The Specialty Exhaust Aftermarket
How Chinese Competitors Are Undercutting U.S. Manufacturers
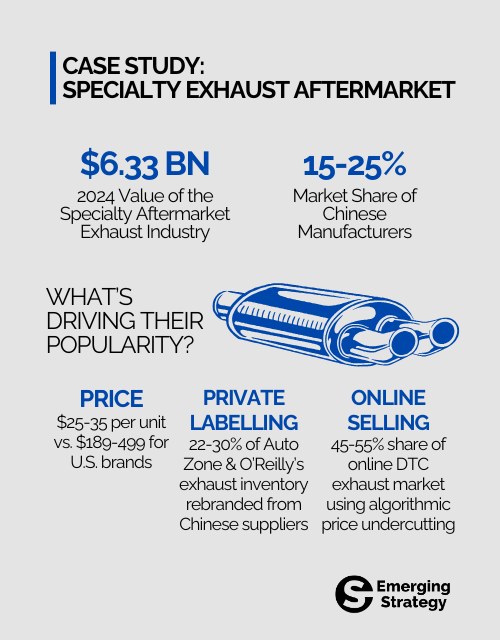
The specialty aftermarket exhaust industry—valued at $6.33 billion in 2024—has become a prime battleground for Chinese penetration. Historically, U.S. manufacturers like MagnaFlow, Borla, and Flowmaster maintained dominance through superior engineering and branding. However, Chinese manufacturers have exploited vulnerabilities to seize 15–25% market share, particularly in the universal/low-cost segment.
Key drivers of this shift include:
- Price Advantage: Chinese exhaust systems sell for as low as $25–35 per unit, compared to $189–499 for U.S. brands.
- Retailer Private Labels: 22–30% of AutoZone and O’Reilly’s exhaust inventory is now sourced from Chinese suppliers, rebranded under house labels.
- E-Commerce Domination: Chinese firms capture 45–55% of the online DTC exhaust market, leveraging algorithmic price undercutting on Amazon and Temu.
Regulatory Asymmetries: The Playing Field Is Not Level
While U.S. manufacturers face stringent EPA and California Air Resources Board (CARB) compliance requirements, Chinese suppliers benefit from lax enforcement and export subsidies. For example:
- Chinese exporters receive 15% production tax rebates under the “Made in China 2025” initiative.
- U.S. environmental regulations, such as the upcoming Advanced Clean Cars II (ACCII) mandate for zero-emission vehicle sales by 2035, threaten to reduce ICE exhaust demand while giving Chinese firms a head start in hybrid-compatible and electric vehicle (EV) thermal management systems.
Strategic Responses for U.S. Aftermarket Firms
Short-Term Defenses
- MAP Enforcement: Deploy AI-driven monitoring systems to detect and remove gray-market listings that violate Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies. Retailers must also be part of the enforcement equation, as Amazon and eBay have shown little willingness to crack down on MAP violators.
- Blockchain Provenance Tracking: Require QR code authentication to verify the metallurgical composition of exhaust components, deterring counterfeits.
Mid-Term Countermeasures
- OEM Lock-In Strategies: U.S. manufacturers must aggressively lock in exclusive partnerships with OEMs, preventing Chinese competitors from gaining further penetration into domestic automaker supply chains.
- Regulatory Advocacy: While reducing loopholes is a priority, manufacturers must prepare for a scenario where these loopholes remain for years. However, they should consider effective lobbying strategies to:
- Lowering the de minimis threshold amount.
- Classifying AliExpress and Temu as “importers of record”, making them liable for defective products.
Long-Term Industry Transformations
- Nearshoring Supply Chains: U.S. manufacturers can shift final assembly operations to Mexico, taking advantage of USMCA’s 0% tariffs (for now!) while maintaining quality control. Chinese firms are also moving production to Mexico to circumvent tariffs. U.S. brands must emphasize quality and warranty advantages to counteract this trend. Simply shifting production to Mexico is not a solution—U.S. firms must ensure nearshoring protects quality, service, and intellectual property, or risk getting undercut by their own suppliers.
- EV Market Adaptation: Exhaust systems companies must pivot towards thermal management and acoustic branding solutions for EVs, ensuring future revenue streams despite ICE market contractions.
The Uneven Battlefield
The U.S. aftermarket auto parts sector are at a crossroads. While Chinese manufacturers exploit pricing advantages, regulatory loopholes, and e-commerce dominance, U.S. firms must accelerate digital tracking, strengthen OEM partnerships, and push for policy reforms. Failure to act decisively could see domestic producers lose an additional 5–7% market share by 2026. The future of the U.S. automotive aftermarket hinges on balancing open competition with strategic protections for domestic innovation and regulatory standards. For U.S. manufacturers, this is about survival. If they don’t adapt fast, some will struggle to survive for the next five years.
Sign up below for our weekly newsletter!
Sources:
- Motor & Equipment Manufacturers Association (MEMA)
- Market sizing data for U.S. automotive aftermarket ($6.33B valuation in 2024)
- Blockchain provenance initiatives (Trusted Supplier program)
- U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC)
- E-commerce loopholes (58% of Chinese parts via DTC, 98.7% uninspected under $800 de minimis rule)
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
- Failure rates of Chinese aftermarket parts (3.2x higher than OEM equivalents)
- 2024 Bipartisan Congressional Investigation
- Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) code misclassification (72% of sampled shipments)
- Annual $1.2B revenue loss for U.S. manufacturers due to tariff evasion
- U.S. Department of Commerce
- Risks of Chinese vehicle connectivity systems (VCS) and remote disabling capabilities
- California Air Resources Board (CARB)
- Advanced Clean Cars II (ACCII) mandate for zero-emission vehicles by 2035
- Made in China 2025 Policy Documents
- 15% production tax rebates for Chinese exporters
- Automotive Aftermarket Retailer Disclosures
- Private-label sourcing (22–30% of AutoZone/O’Reilly exhaust inventory from Chinese suppliers)
- E-Commerce Platform Analytics
- Pricing data for Chinese exhaust systems ($25–35 vs. U.S. $189–499)
- Algorithmic undercutting on Temu/AliExpress
- U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) Trade Data
- Nearshoring strategies to leverage 0% tariffs







